Η επώδυνη τροπική νόσος τσικουνγκούνια μπορεί πλέον να μεταδοθεί από κουνούπια στο μεγαλύτερο μέρος της Ευρώπης, σύμφωνα με νέα επιστημονική μελέτη, η οποία καταγράφει τη διεύρυνση των γεωγραφικών περιοχών όπου ευνοούνται οι συνθήκες μετάδοσης.
Η έρευνα αποδίδει την εξέλιξη αυτή στην κλιματική κρίση και στην εξάπλωση του ασιατικού κουνουπιού-τίγρη και καταλήγει στο συμπέρασμα ότι οι υψηλότερες θερμοκρασίες επιτρέπουν τη μετάδοση του ιού για μεγαλύτερο χρονικό διάστημα μέσα στο έτος, ακόμη και σε χώρες που μέχρι πρόσφατα θεωρούνταν ότι βρίσκονταν εκτός της ζώνης κινδύνου.
Χαμηλότερο όριο θερμοκρασίας για επώαση, μεγαλύτερος κίνδυνος
Η μελέτη, που δημοσιεύθηκε στην επιθεώρηση Journal of the Royal Society Interface , είναι η πρώτη που αξιολογεί πλήρως την επίδραση της θερμοκρασίας στον χρόνο επώασης του ιού τσικουνγκούνια μέσα στο κουνούπι-τίγρη (Aedes albopictus).
Οι ερευνητές διαπίστωσαν ότι το κατώτατο όριο θερμοκρασίας για να καταστεί δυνατή η μετάδοση του ιού είναι μεταξύ 13°C και 14°C – δηλαδή 2,5 βαθμούς Κελσίου χαμηλότερο από προηγούμενες εκτιμήσεις (16-18°C). Η διαφορά αυτή χαρακτηρίζεται «σοκαριστική», καθώς μεταφράζεται σε σημαντική διεύρυνση των γεωγραφικών περιοχών και των χρονικών περιόδων όπου μπορεί να υπάρξει μετάδοση της νόσου τσικουνγκούνια.
Σύμφωνα με τα νέα δεδομένα, η μετάδοση μπορεί να είναι εφικτή για περισσότερο από έξι μήνες τον χρόνο σε χώρες όπως η Ισπανία, η Πορτογαλία, η Ιταλία και η Ελλάδα, ενώ για τρεις έως πέντε μήνες σε κράτη όπως το Βέλγιο, η Γαλλία, η Γερμανία και η Ελβετία. Ακόμη και στη νοτιοανατολική Αγγλία, το «παράθυρο» κινδύνου εκτιμάται πλέον σε περίπου δύο μήνες ετησίως.
Πώς μεταδίδεται ο ιός τσικουνγκούνια και ποια τα συμπτώματα της νόσου
Ο ιός τσικουνγκούνια εντοπίστηκε για πρώτη φορά το 1952 στην Τανζανία και μέχρι πρότινος περιοριζόταν κυρίως σε τροπικές περιοχές, όπου καταγράφονται εκατομμύρια λοιμώξεις κάθε χρόνο.
Η νόσος προκαλεί έντονους και παρατεταμένους πόνους στις αρθρώσεις, που μπορεί να διαρκέσουν μήνες ή και χρόνια, ενώ σε μικρά παιδιά και ηλικιωμένους μπορεί να αποβεί θανατηφόρα.
Καθοριστικό ρόλο στην εξάπλωση του ιού στη Γηραιά Ήπειρο διαδραματίζει το ασιατικό κουνούπι-τίγρης (Aedes albopictus), ένα ιδιαίτερα επεμβατικό είδος, που τσιμπά κατά τη διάρκεια της ημέρας και έχει εγκατασταθεί τις τελευταίες δεκαετίες σε πολλές περιοχές της νότιας και κεντρικής Ευρώπης.
Η μετάδοση γίνεται όταν ένα κουνούπι τσιμπήσει μολυσμένο άτομο και ο ιός τσικουνγκούνια περάσει στο έντερό του. Έπειτα από μια περίοδο επώασης, ο ιός εντοπίζεται στο σάλιο του κουνουπιού, επιτρέποντας τη μετάδοσή του στον επόμενο άνθρωπο που θα τσιμπήσει. Αν όμως η περίοδος επώασης είναι μεγαλύτερη από το προσδόκιμο ζωής του εντόμου, η αλυσίδα μετάδοσης διακόπτεται. Η άνοδος της θερμοκρασίας επιταχύνει αυτή τη διαδικασία, αυξάνοντας τις πιθανότητες εξάπλωσης.
Οι επιστήμονες προειδοποιούν ότι η Ευρώπη θερμαίνεται με ρυθμό σχεδόν διπλάσιο από τον παγκόσμιο μέσο όρο, γεγονός που καθιστά «ζήτημα χρόνου»την περαιτέρω εξάπλωση του ιού σε βορειότερες περιοχές της Γηραιάς Ηπείρου.
Ήδη μεγάλες εστίες σε Γαλλία και Ιταλία
Τα τελευταία χρόνια έχουν καταγραφεί περιορισμένα κρούσματα της νόσου τσικουνγκούνια σε περισσότερες από δέκα ευρωπαϊκές χώρες. Ωστόσο, το 2025 σημειώθηκαν μεγάλες επιδημίες εκατοντάδων κρουσμάτων στη Γαλλία και την Ιταλία.
Στη Γαλλία, μέχρι πρότινος είχαν καταγραφεί περίπου 30 κρούσματα σε διάστημα δεκαετίας. Μόνο την περασμένη χρονιά, όμως, τα περιστατικά ξεπέρασαν τα 800. Πολλά από τα αρχικά κρούσματα συνδέθηκαν με ταξιδιώτες που επέστρεψαν από υπερπόντια εδάφη, όπως η Ρεϊνιόν, όπου βρίσκονταν σε εξέλιξη επιδημίες της νόσου τσικουνγκούνια.
Μέχρι σήμερα, οι ψυχροί ευρωπαϊκοί χειμώνες λειτουργούσαν ως φυσικό «φρένο», περιορίζοντας τη δραστηριότητα των κουνουπιών. Όμως οι επιστήμονες παρατηρούν ήδη δραστηριότητα όλο τον χρόνο σε περιοχές της νότιας Ευρώπης, γεγονός που ενδέχεται να οδηγήσει σε μεγαλύτερες και συχνότερες επιδημίες.
Η σημασία της πρόληψης και της επιτήρησης
O Παγκόσμιος Οργανισμός Υγείας (ΠΟΥ) επισημαίνει ότι η μελέτη αποτελεί σοβαρή ένδειξη πως η μετάδοση του ιού τσικουνγκούνια στην Ευρώπη θα γίνει πιο εμφανής με την πάροδο του χρόνου. Σύμφωνα με ειδικούς του ΠΟΥ έως και το 40% των ασθενών ενδέχεται να συνεχίσουν να υποφέρουν από αρθρίτιδα ή έντονο πόνο ακόμη και πέντε χρόνια μετά τη μόλυνση.
Παρότι υπάρχουν εμβόλια, το κόστος τους είναι υψηλό και η βασική γραμμή άμυνας παραμένει η αποφυγή των τσιμπημάτων. Οι ειδικοί συνιστούν την απομάκρυνση στάσιμων νερών όπου αναπαράγονται τα κουνούπια, τη χρήση εντομοαπωθητικών και την επιλογή μακριών, ανοιχτόχρωμων ρούχων.
Παράλληλα, υπογραμμίζεται η ανάγκη ενίσχυσης των συστημάτων επιτήρησης, ώστε οι τοπικές Αρχές να γνωρίζουν πότε και πού υπάρχει αυξημένος κίνδυνος. Η λεπτομερής χαρτογράφηση των περιοχών και των μηνών πιθανής μετάδοσης της νόσου τσικουνγκούνια παρέχει πλέον στα κράτη ένα κρίσιμο εργαλείο έγκαιρης παρέμβασης.
Οι επιστήμονες προειδοποιούν ότι η αποτροπή μόνιμης εγκατάστασης του κουνουπιού-τίγρη σε νέες περιοχές αποτελεί καθοριστικό παράγοντα για την αποφυγή μιας νέας υγειονομικής πρόκλησης στην Ευρώπη.
Πηγή: iefimerida.gr
Chikungunya Fever Spreads Across Europe Due to Climate Change
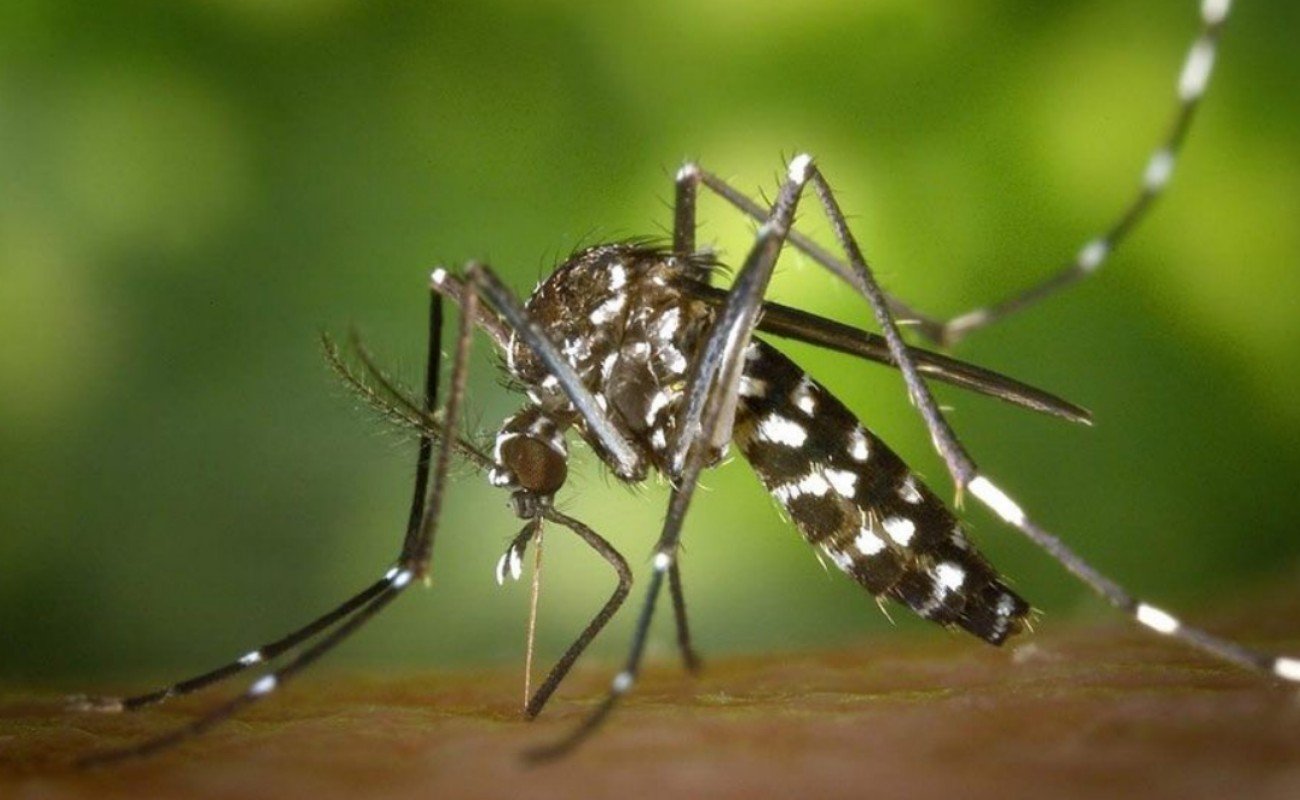
A new scientific study warns that the tropical disease chikungunya can now be transmitted by mosquitoes across much of Europe, due to the climate crisis and the spread of the Asian tiger mosquito. The study, published in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface, found that the lower temperature limit for virus incubation is lower than previously thought (13-14°C instead of 16-18°C), significantly expanding the areas and periods of transmission. According to the new data, transmission may be possible for more than six months a year in countries such as Spain, Portugal, Italy and Greece, while in others, such as Belgium, France, Germany and Switzerland, for three to five months. Even in southeastern England, the risk is estimated to be around two months a year. The chikungunya virus was first identified in 1952 in Tanzania and causes severe joint pain, which can last for months or years, and can be fatal in children and the elderly. The spread of the virus is directly linked to the Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus), an invasive species that has established itself in many European countries. The virus is transmitted when a mosquito bites an infected person and then a healthy one. Rising temperatures accelerate the incubation process of the virus within the mosquito, increasing the likelihood of spread. Scientists warn that Europe is warming at a faster rate than the global average, making further spread of the virus inevitable. The study highlights the need for increased vigilance and preventive measures to address the threat posed by chikungunya to the European continent.
You Might Also Like

Νορβηγία: Παρά το λιώσιμο των πάγων, οι πολικές αρκούδες γίνονται πιο παχιές και υγιείς
Feb 7

Οι αδυναμίες στα ηλεκτρικά δίκτυα ακριβαίνουν το ρεύμα στην Ευρώπη
Feb 13

Bloomberg: Η Eυρώπη εξετάζει την ανάπτυξη πυρηνικού οπλοστασίου
Feb 13

Bloomberg: Η Eυρώπη εξετάζει την ανάπτυξη πυρηνικού οπλοστασίου
Feb 13

Καταιγίδα Νιλς: Σαρώνει την Ευρώπη – Δύο νεκροί σε Γαλλία και μία στην Ισπανία (εικόνες)
Feb 13